
Lesser known cannabinoids and terpenes may be helpful for patients. Here the author shows why, and how patients can choose more effective medical cannabis products.

Lesser known cannabinoids and terpenes may be helpful for patients. Here the author shows why, and how patients can choose more effective medical cannabis products.
There are thousands of other potential analytical targets in cannabis that are relatively unexplored. Here, the author examines terpenes.
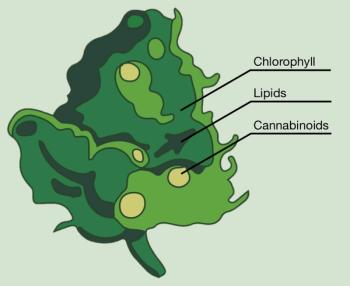
At a glance, modern extraction machines can seem a little mysterious: plant material is added to an extraction chamber, processing parameters are chosen, the extraction process is carried out, and an output of material is collected. Part I of this series examines the two main biologically-inherent starting-material influences.

Here the LC–UV separation of 16 cannabinoids of interest was performed while the potential impact from minor cannabinoids and terpenes on reported potency values was monitored.


Headspace SPME combined with GC–MS for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of terpenes in cannabis offers several advantages compared to other methods. It does not require the use of organic solvents, does not coextract matrix, and provides additional means of peak identification and purity using spectral data. It is also a nondestructive method.

QuEChERS is introduced to the discipline of forensic testing as a viable method for the extraction of pesticides and cannabinoids in various complex sample matrices

An interview with Cindy Orser

An interview with Montel Williams

An interview with Jeffrey C. Raber